
Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes (ACM) is a solution designed to manage multiple Kubernetes clusters from a single interface. It provides centralized visibility, control and governance across hybrid and multi-cloud environments. It also improves application and cluster management.
The key features of the ACM are cluster lifecycle management, policy enforcement, multicluster observability, support for the cloud providers, integration with Ansible and/or integration with OpenShift GitOps/Argo CD.
It simplifies multicluster management, while enhancing security, compliance and operational efficiency across different environments.
In this tutorial, I will show how to configure Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes (ACM) in the OpenShift cluster.
Requirements:
- OpenShift Container Platform must have access to the Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management operator from the OperatorHub catalog, which is essential for deploying ACM;
- Supported OpenShift Container Platform and the OpenShift Container Platform CLI;
- Access to the catalog.redhat.com;
- Administrator-level access (cluster-admin);
1. Installation and configuration of Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes Operator
Red Hat OpenShift Operators are extensions (essentially there are a custom controllers) mechanism designed to automate the management of Kubernetes-native applications within the OpenShift platform. They enable the creation, configuration, and management of application instances in a way that simplifies operations and enhances the user experience.
1. Log in to the Red Hat OpenShift console. The account must have cluster-admin privileges.

2. Go to the OperatorsHub under Operators tab.
There, you can find all available Operators. In the search box type: Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes. When the ACM operator appears, click on it.
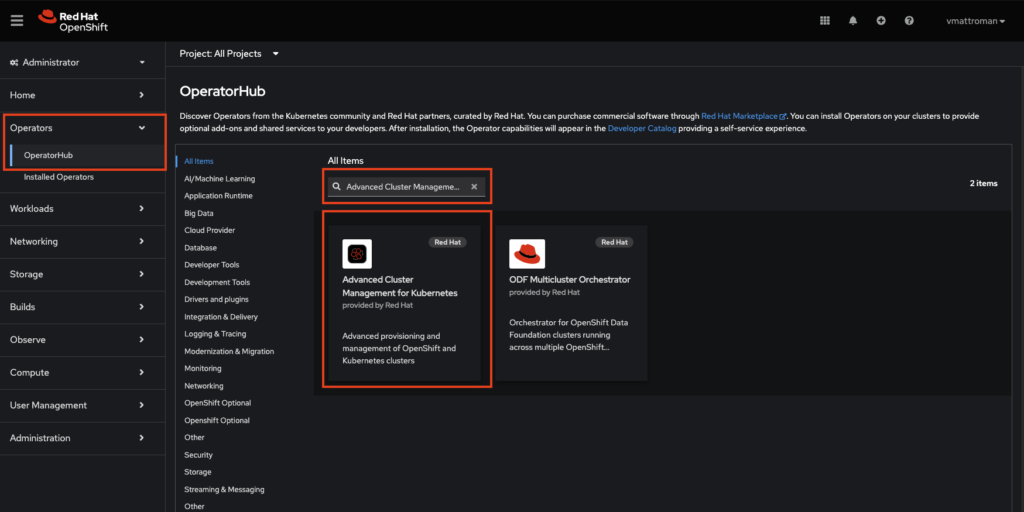
3. This is a description of Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes Operator. Leave a default Channel and Version. Review the details and click on Install button.

4. Leave all default settings in the Installation mode and Installed Namespace. ACM needs a dedicated namespace (project) that will be created during deployment. Click on Install button.

5. Operator installation in progress. You can monitor the status by clicking the blue link View installed Operators in Namespace open-cluster-management.
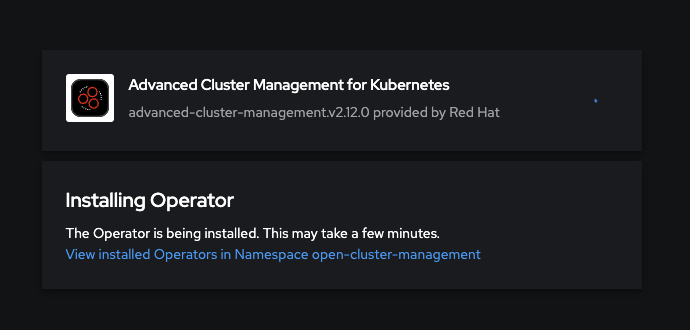

6. Operator was installed and status changed to Succeed. Click on the Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes Operator.

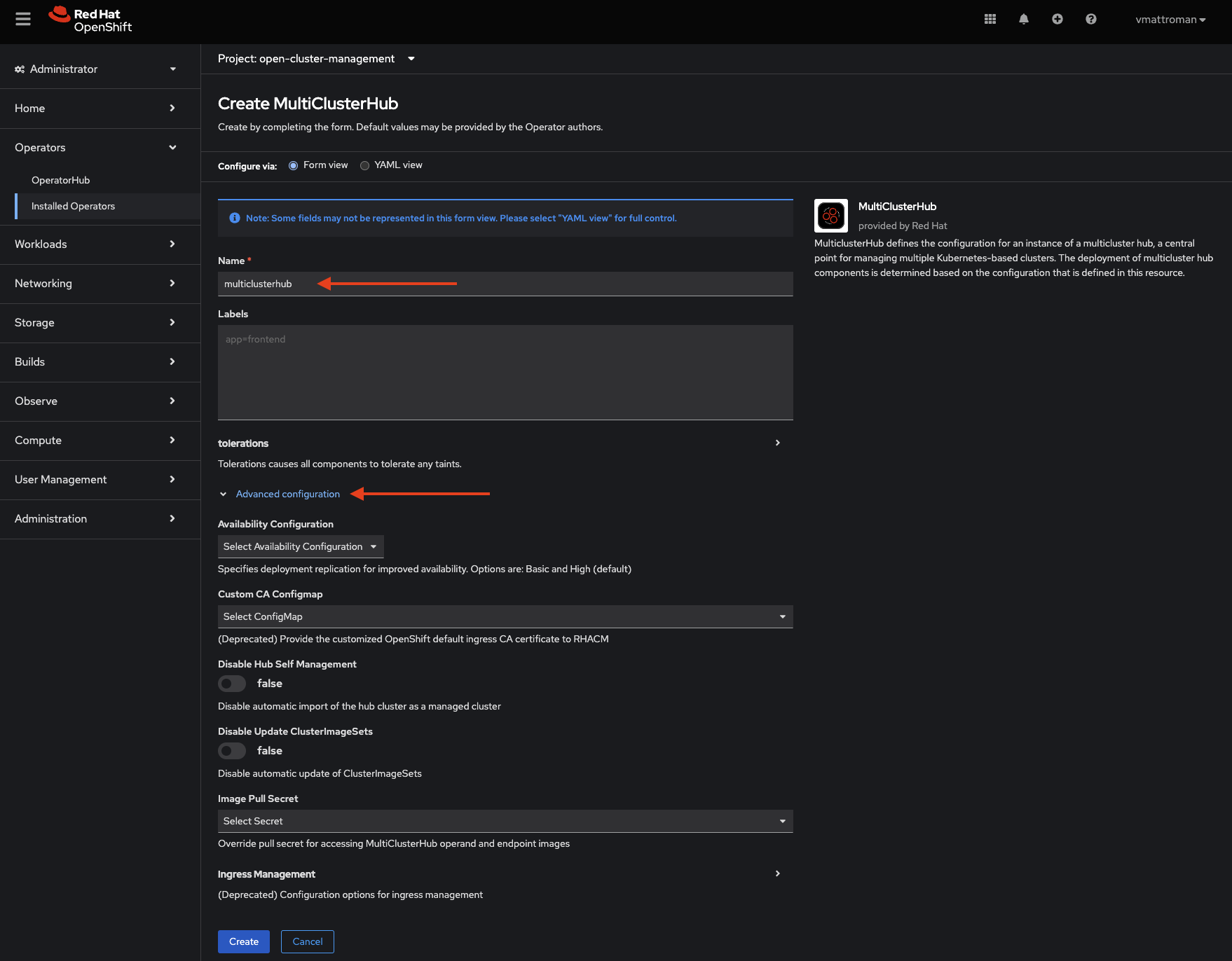
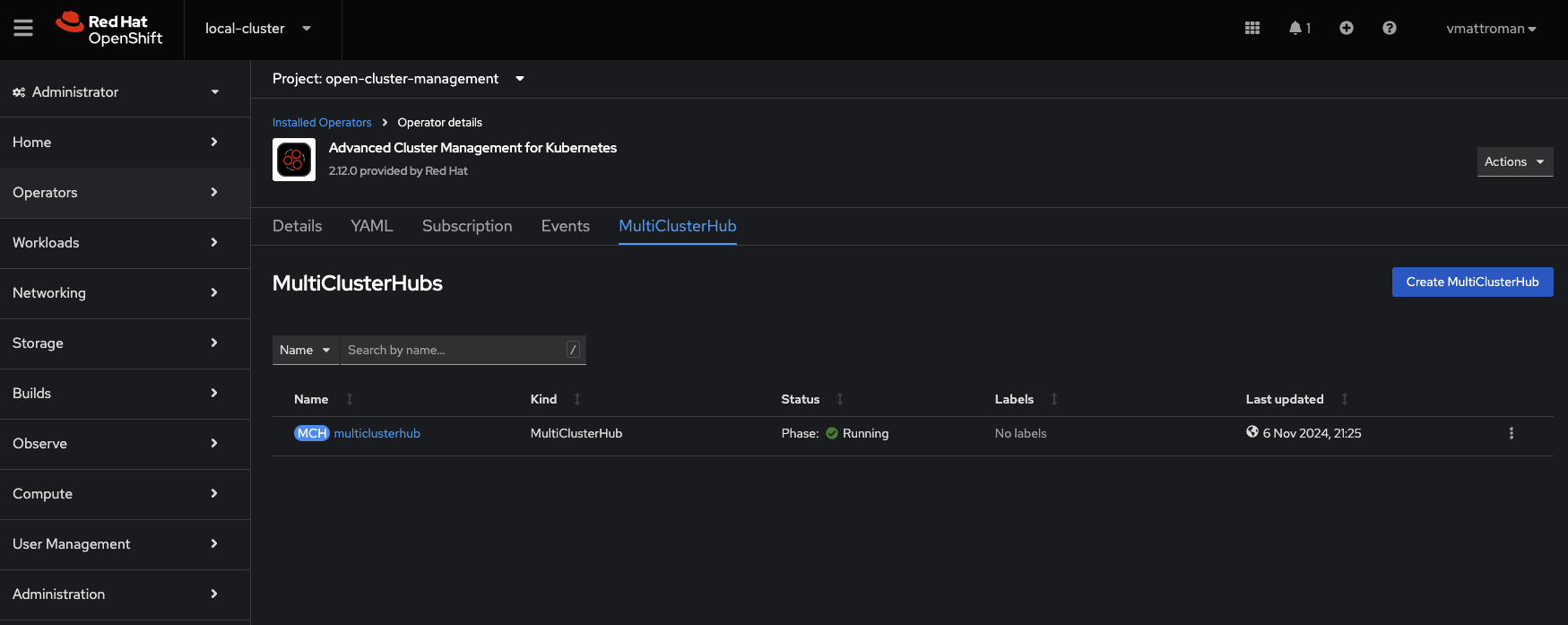
7. Now, we need to create MultiClusterHub custom resource. This kind of resource provides centralized management capabilities for Kubernetes clusters across various environments. Move to the MultiClusterHub tab.

8. Click on the Create MultiClusterHub button.

9. Review the installation details. Leave the name as is. Optionally, if you want to configure additional/advanced features, expand Advanced configuration section and edit desired values. Click Create button.
10. Instillation in progress. You can monitor the status in the Installed Operators tab or in Pods section under Workloads.
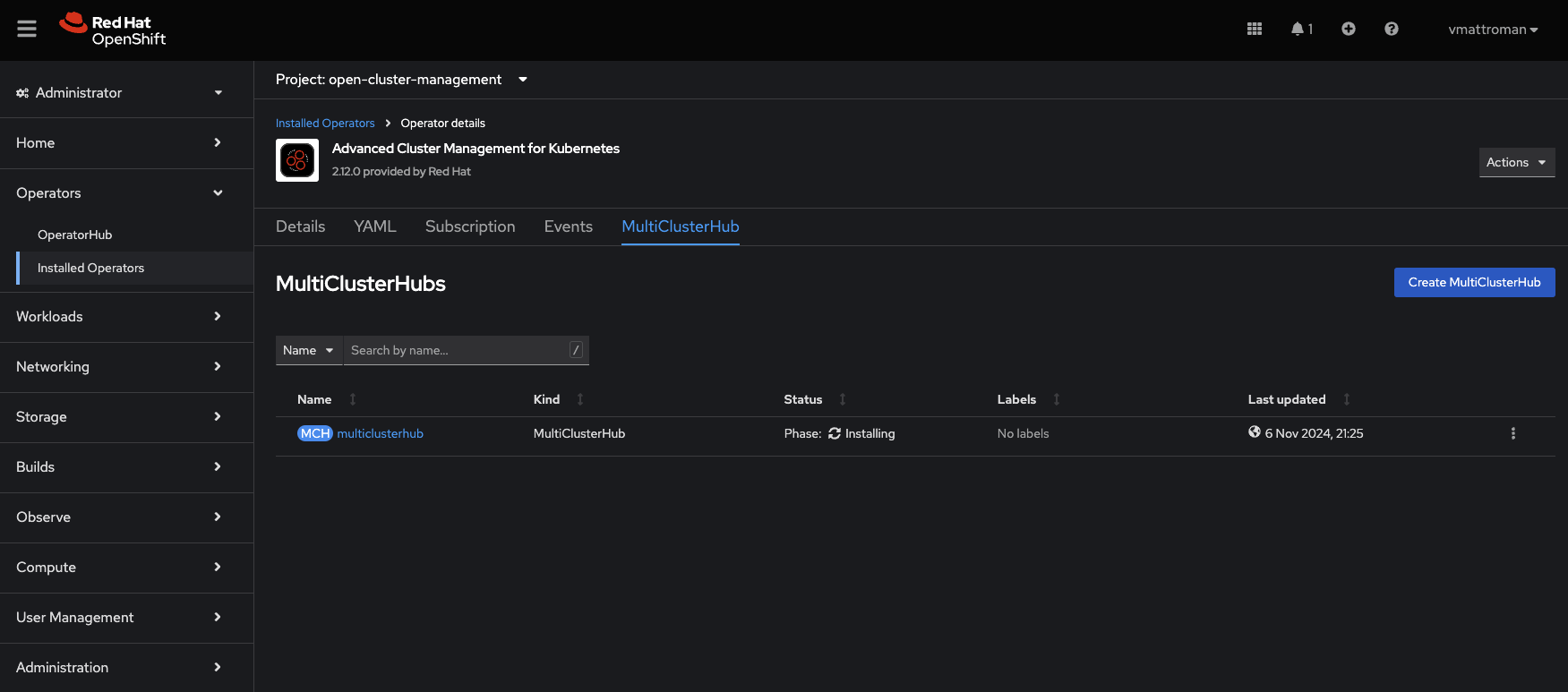

11. Instillation completed. ACM Operator is up and ready! 😉
2. Accessing ACM console
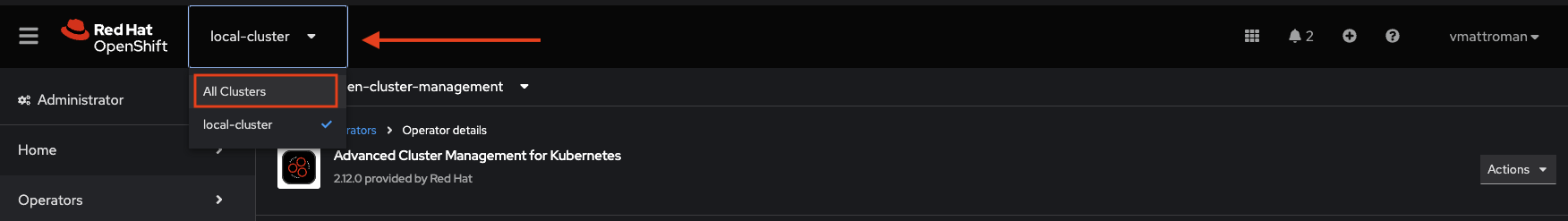
1. After installation of Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes Operator, you can find a new drop down list near the Red Hat OpenShift logo. From there, we can switch between local cluster (aka hub cluster) which is a current cluster and All Clusters option. All Clusters redirect to the ACM view.
2. During the first visit to ACM, a new window appears with three possibilities:
– Import an existing cluster – if we have some another existing OpenShift clusters, we can import it to the ACM;
– Connect you cloud provider – to manage Red Hat OpenShift clusters running on cloud providers like Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform or bare metal, you need to create the provider connection;
– Discover hosts to create host inventory – use this option if you want to create a centralized repository that tracks all the bare metal hosts available for cluster provisioning and management within OpenShift.
In this case, I don’t have any other clusters to add. Close this window with an X.

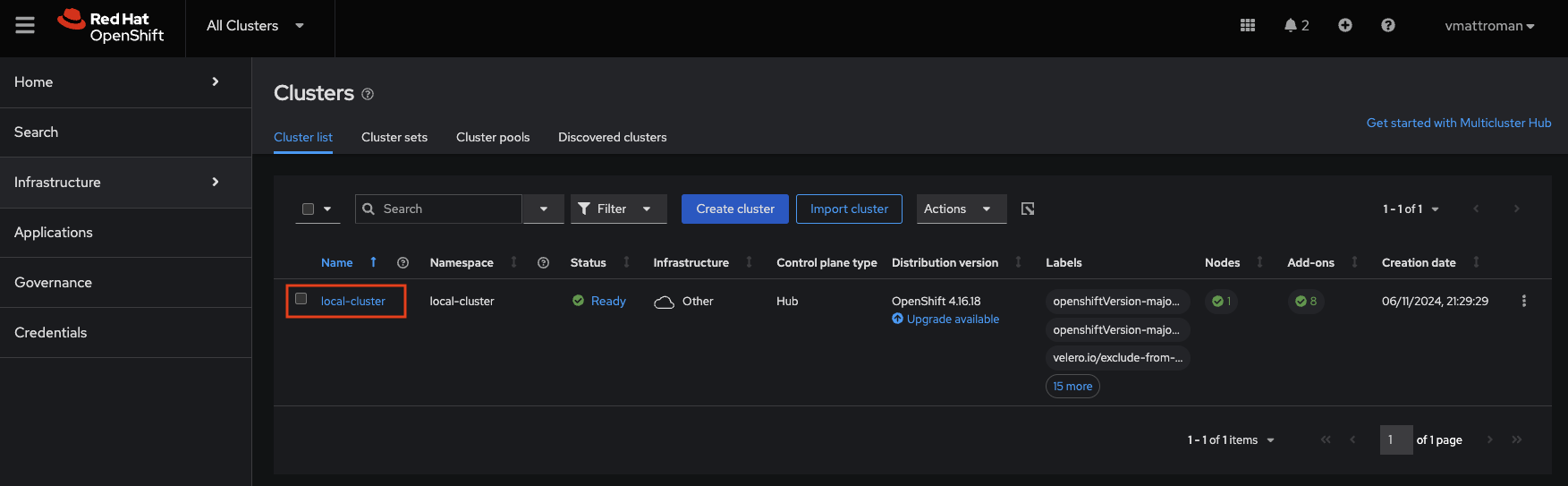
3. Here, in the Cluster list tab we will see all existing/attached OpenShift clusters. Of course, in this configuration there is only one, single (current) local-cluster. To get more details, click in the name.
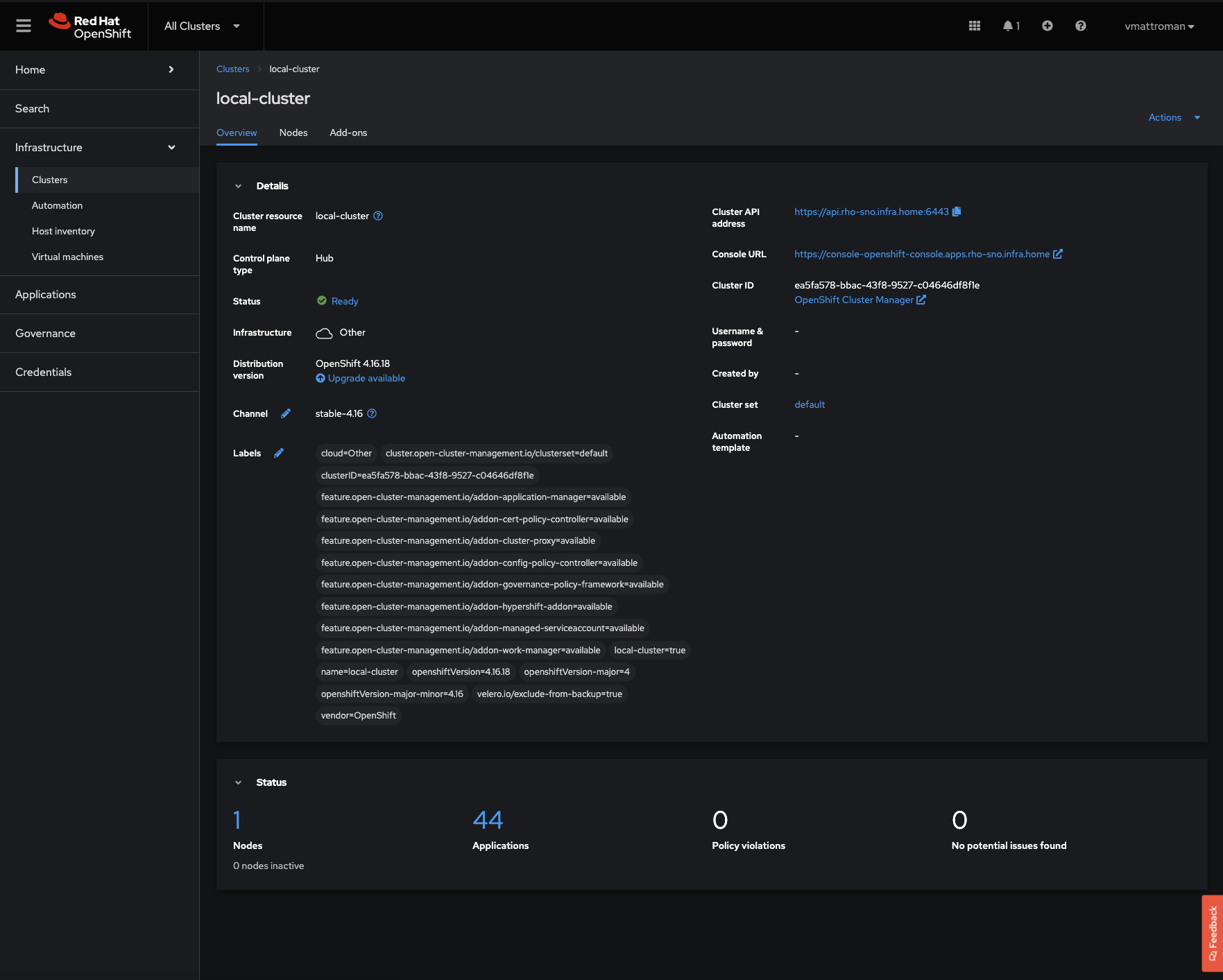
4. To get additional data, go to the Overview tab. There is summary about number of attached OpenShift Clusters, Nodes, Total number of applications and some Insights.
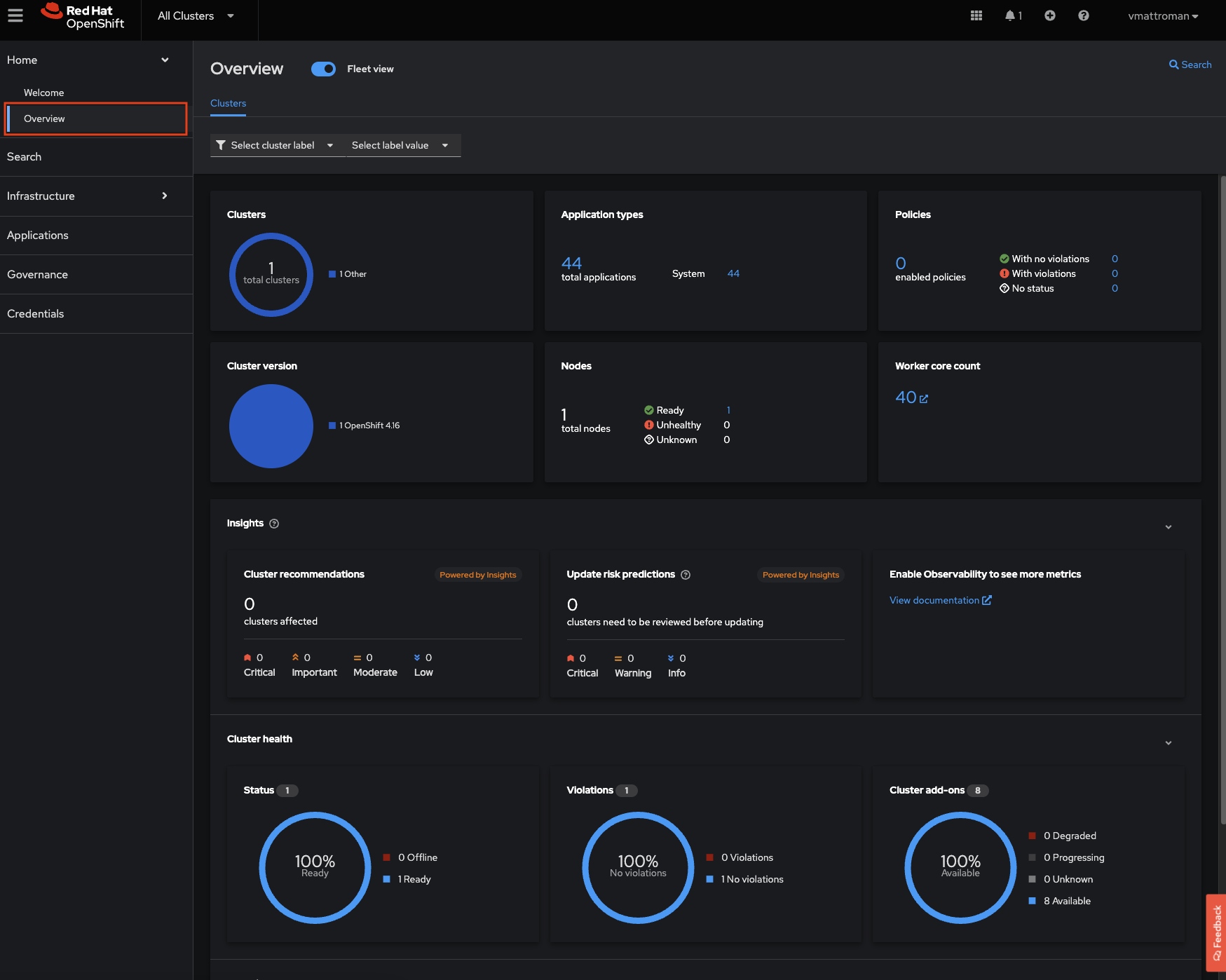
Summary
In summary, Red Hat OpenShift Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes is an essential tool for organizations leveraging Kubernetes at scale across diverse environments.
Keep looking at my blog, new posts are coming! There is so much more great features to explore 😉





































One Comment