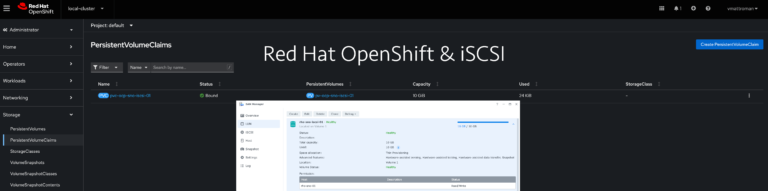
Red Hat OpenShift – Configuring Virtualization
Red Hat OpenShift Virtualization is a feature integrated into the Red Hat OpenShift platform acting as Operator. It’s designed to allow organizations to run and manage both: virtual machines (VMs) and container workloads side by side. This capability provides a modern approach to infrastructure management, enabling seamless migration and operation of traditional VM workloads within a cloud-native environment.